
The buzz around Generative AI (GenAI) is undeniable. From crafting compelling marketing copy to generating intricate code, Large Language Models (LLMs) are rapidly transforming workflows. However, beneath the surface of impressive text generation lies a critical challenge: reliability and factual accuracy. Standalone LLMs, trained on vast but static datasets, can hallucinate or provide outdated information, limiting their utility in enterprise environments where truth and timeliness are paramount.
Enter Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).
This powerful paradigm enhances LLMs by equipping them with the ability to access and incorporate external, up-to-date information into their responses. Think of it as giving the LLM a real-time open-book test, ensuring its answers are grounded in verifiable data. But how do we make this “open book” truly dynamic, reflecting the ever-changing landscape of enterprise knowledge? The answer lies in the real-time streaming capabilities of Apache Kafka.
The Limitations of Static Knowledge in LLMs
LLMs possess an incredible capacity to understand and generate human-like text. However, their knowledge is bound by the data they were trained on, which is often a snapshot in time. This can lead to several issues:
- Outdated Information: The model might not be aware of recent events, product updates, or policy changes.
- Hallucinations: Without grounding in specific data, LLMs can sometimes generate plausible-sounding but factually incorrect information.
- Lack of Contextual Specificity: General-purpose LLMs may struggle to provide answers tailored to an organization’s unique internal knowledge base.
RAG: Bridging the Gap with External Knowledge
RAG addresses these limitations by introducing a retrieval step before text generation. When a user poses a question, the RAG system first retrieves relevant documents or data snippets from an external knowledge base (e.g., internal wikis, product catalogs, customer support tickets). This retrieved information is then appended to the original prompt, providing the LLM with the necessary context to generate a more accurate and informed response.
Traditional RAG implementations often rely on batch processing of data to update the knowledge base. This means there’s a delay between when information is created or updated and when it becomes available to the LLM, creating a window of potential inaccuracy. This is where Kafka steps in to revolutionize the process.
Kafka: The Real-Time Nervous System for Live RAG
To truly unlock the potential of RAG in dynamic enterprise environments, we need to ensure the knowledge base is constantly up-to-date. This is where Kafka’s strength in handling high-throughput, low-latency streaming data becomes invaluable.
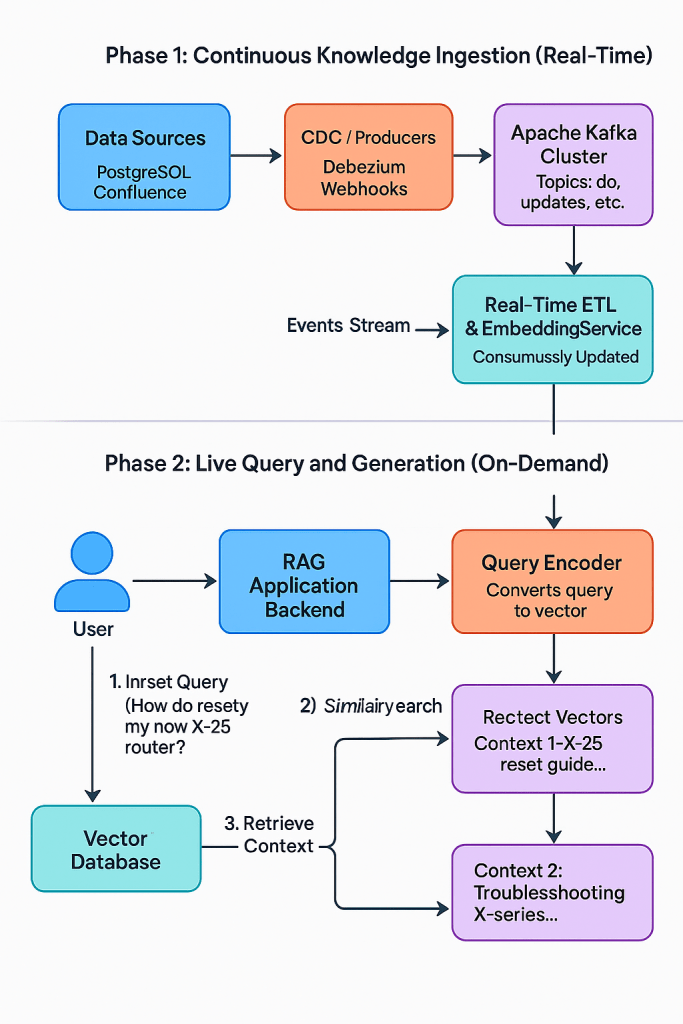
Imagine a Live RAG architecture powered by Kafka:
- Real-time Data Ingestion: Any change or new piece of information within the organization is captured as an event and streamed into Kafka topics. This could include updates to product databases (using Change Data Capture – CDC tools like Debezium), new entries in a knowledge base, or even real-time customer interactions.
- Continuous Knowledge Base Updates: A dedicated service consumes these Kafka streams and uses them to continuously update the underlying knowledge base. This often involves updating vector embeddings in a vector database, ensuring the retrieved information is always the most current.
- Dynamic Retrieval: When a user asks a question, the RAG system queries this constantly updated knowledge base to retrieve the most relevant context.
- Augmented Prompt and Generation: The retrieved information is seamlessly incorporated into the prompt sent to the LLM, enabling it to generate responses that are not only relevant but also based on the latest available data.
Benefits of Live RAG with Kafka
This real-time approach to RAG offers several significant advantages:
- Unparalleled Accuracy: By grounding LLM responses in continuously updated data, Live RAG minimizes the risk of hallucinations and outdated information.
- Enhanced Contextual Relevance: The LLM always has access to the most recent context, leading to more precise and helpful answers.
- Real-time Responsiveness: Critical information is immediately reflected in the LLM’s knowledge, enabling real-time applications like customer support with up-to-the-minute details.
- Scalability and Reliability: Kafka’s distributed and fault-tolerant nature ensures the robustness and scalability of the Live RAG pipeline.
- Reduced Latency: By streamlining the knowledge update process, Kafka contributes to a faster overall RAG experience.
Building a Live RAG Pipeline with Kafka: Key Components
Implementing a Live RAG system with Kafka involves several key components:
- Kafka Cluster: The central nervous system for streaming data events.
- Data Source Connectors (e.g., Debezium): To capture real-time changes from databases and other data sources and publish them to Kafka.
- Stream Processing Engine (e.g., Kafka Streams, Flink): To consume Kafka streams, perform any necessary data transformations, and update the knowledge base.
- Vector Database: To store and efficiently query vector embeddings of the knowledge base.
- RAG Framework (e.g., LangChain, Haystack): To orchestrate the retrieval and generation steps.
- LLM: The core generative model.
Live Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Kafka represents a significant step forward in making Generative AI truly enterprise-grade. By ensuring LLMs have access to a continuously updated and reliable knowledge base, organizations can unlock the full potential of GenAI for a wide range of applications, from intelligent chatbots and personalized recommendations to real-time knowledge management and beyond. As the demand for accurate and timely information continues to grow, Kafka will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of intelligent systems.
Leave a comment