Photocredits :https://arxiv.org/pdf/2208.07638.pdf
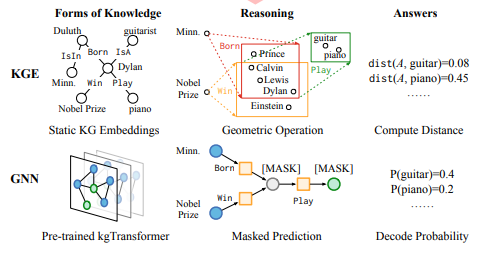
Knowledge graphs (KGs) have emerged as a powerful tool for representing and reasoning over semantic knowledge. They consist of entities, relationships, and attributes, which can be used to model a wide variety of domains, such as science, medicine, and finance. However, the inherent shallowness and static nature of KG embeddings limit their ability to handle complex logical queries, which involve logical operators, imputed edges, multiple source entities, and unknown intermediate entities.
To address these limitations, we have the Knowledge Graph Transformer (kgTransformer), a novel framework that combines masked pre-training and fine-tuning strategies to enhance the reasoning capabilities of KG transformers. kgTransformer employs a KG triple transformation method to adapt the Transformer architecture to KGs and utilizes a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) sparse activation mechanism to improve its efficiency. Furthermore, a two-stage masked pre-training strategy is used to enhance transferability and generalizability by formulating complex logical queries as masked prediction tasks.
The paper addresses the challenges posed by complex logical queries, which involve logical operators, imputed edges, multiple source entities, and unknown intermediate entities. Traditional KG embeddings struggle with these queries due to their shallow and static architectures. The authors argue that existing models cannot effectively handle the growing complexity of logical queries in KGs.
Contributions:
- Architecture Design: The kgTransformer architecture is designed to effectively encode KGs, addressing the limitations of existing models in handling complex logical queries.
- Triple Transformation Method: The introduction of the Triple Transformation method enables the model to handle relations in KGs, contributing to its ability to reason over complex queries.
- Mixture-of-Experts Strategy: The integration of the MoE strategy allows the model to scale up parameters without sacrificing computational efficiency.
- Masked Pre-Training Framework: The masked pre-training framework enhances the model’s generalizability by formulating complex logical queries as a masked prediction problem.
Proposed Solution:
kgTransformer Architecture:
The kgTransformer is introduced as a Transformer-based Graph Neural Network (GNN) designed to handle KGs. It utilizes a Triple Transformation method to enable the Transformer to deal with relations in KGs efficiently. This involves turning relations into relation-nodes, transforming the KG into a directed graph without edge attributes. The architecture is further enhanced by the Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) sparse activation strategy, allowing the model to scale up parameters while maintaining computational efficiency.
Architecture Overview:
- Motivation for Masked Pre-training and Fine-tuning:
- The goal is to improve the generalizability of kgTransformer for KG reasoning.
- Two-stage pre-training: Initialization and Refinement.
- Two-Stage Pre-training: Initialization and Refinement:
- Existing reasoners often have low coverage over entities and relations in training, leading to poor transferability.
- Stage 1 (Dense Initialization): Randomly sample arbitrary-shaped masked subgraphs from the original KGs. Use random walk strategies (RWR and tree-based RWR) to sample dense query subgraphs.
- Stage 2 (Sparse Refinement): Further refine the model’s ability for small and sparse queries using meta-graph sampling for common query types (1p, 2p, 3p, 2i, and 3i).
- Fine-tuning:
- After pre-training, fine-tuning is performed on downstream reasoning tasks.
- Fine-tuning loss is formulated for masked prediction based on feasible answers for a query graph.
- Out-of-domain Generalization:
- Four specific types of out-of-domain queries (ip, pi, 2u, up) are provided in the validation and test sets.
- Different strategies are used to handle disjunctive/union queries (2u, up).
Masked Pre-Training:
To improve the generalizability of kgTransformer, the authors introduce a masked pre-training framework. Complex logical queries are formulated as a masked prediction problem. During pre-training, subgraphs are randomly sampled from KGs, and random entities are masked for prediction. The pre-training involves two stages: dense initialization, focusing on enriching the model with dense and arbitrary-shaped contexts, and sparse refinement, trained on sparse and clean meta-graphs to bridge the gap between pre-training and downstream queries.
KG Triple Transformation
To enable the Transformer architecture to effectively process KGs, a KG triple transformation method is introduced that converts KG triples into a suitable format for Transformer input. This transformation involves representing entities as vectors, relationships as one-hot vectors, and incorporating edge directions.
Mixture-of-Experts Sparse Activation
KGs are inherently sparse, with a large proportion of zero-valued entries in the adjacency matrix. To address this sparsity, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) sparse activation mechanism is employed, which dynamically selects a subset of experts to compute the activation for each node, reducing computational cost without sacrificing accuracy.
Two-Stage Masked Pre-training
Traditional pre-training methods for KG transformers typically mask entities or relationships to generate training examples. However, these methods may struggle with complex logical queries that involve multiple source entities and unknown intermediate entities. To address this, a two-stage masked pre-training strategy is used. In the first stage, the entities are masked to learn basic entity-relationship interactions. In the second stage, the subgraphs are masked to capture more complex relationships and reasoning patterns.
The paper presents kgTransformer, a Transformer-based graph neural network architecture for handling EPFO queries on KGs. kgTransformer is trained using a masked pre-training framework, which involves formulating complex logical queries as masked prediction problems. The paper demonstrates that kgTransformer outperforms state-of-the-art KGE-based approaches on nine in-domain and out-of-domain downstream reasoning tasks. Additionally, the paper shows that masked pre-training can endow kgTransformer’s reasoning with explainability and interpretability.
The masked pre-training consists of two stages: dense initialization and sparse refinement. The dense initialization stage aims to enable kgTransformer with the general knowledge in KGs via masked pre-training over dense and large sampled subgraphs. The sparse refinement stage further refines its ability for small and sparse queries during inference.
Experimental Evaluation
The authors conduct extensive experiments on two benchmark datasets, namely FB15k-237 and NELL995. The kgTransformer consistently outperforms both KG embedding-based baselines and advanced encoders across nine in-domain and out-of-domain reasoning tasks. The model’s ability to provide reasoning paths contributes to its interpretability and explainability
- Datasets:
- Evaluation is done on FB15k-237 and NELL995 datasets with nine reasoning challenges, including both in-domain and out-of-domain queries.
- Query-answer datasets are constructed for logic query reasoning.
- Evaluation Protocol:
- Follows the protocol in Query2Box, including the filtering setting and metrics calculation.
- Main Results:
- kgTransformer is compared with various methods based on Knowledge Graph Embeddings (KGEs) and sequence encoders.
- Achieves competitive or superior results on both datasets, outperforming existing methods like GQE, Q2B, EmQL, and CQD.
- Ablation Study:
- Analyzes the necessity of two-stage pre-training and the function of fine-tuning through ablation studies.
- Demonstrates that both pre-training and fine-tuning contribute to improving model capacity.
- Hyperparameter Analysis:
- Studies the impact of hyperparameters, including the number of layers, hidden size, label smoothing, and the number of experts.
- Highlights the importance of proper model depth, hidden size, and label smoothing.
- Efficiency Analysis:
- Multi-expert models significantly increase model capacity with limited computational cost.
The paper presents a comprehensive solution, kgTransformer, for addressing the challenges associated with complex logical queries in KGs. The combination of a novel architecture, Triple Transformation method, MoE strategy, and masked pre-training framework contributes to the model’s superior performance compared to existing approaches. The research not only advances the state-of-the-art in KG reasoning but also opens avenues for further exploration in handling complex queries in diverse domains. Moreover, kgTransformer’s explainability feature provides valuable insights into the reasoning process, making it a valuable tool for knowledge discovery and reasoning in KGs.
Leave a comment