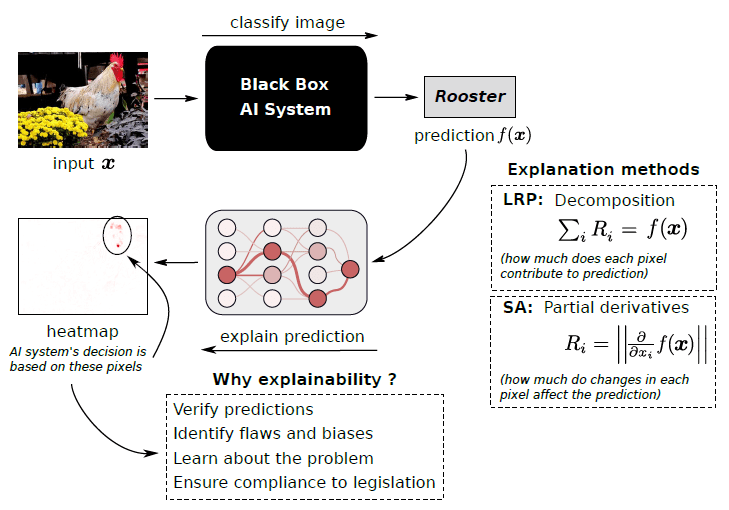
Deep learning models have become increasingly powerful and successful in recent years, but they can also be complex and difficult to understand. This can make it challenging to trust their decisions, especially in critical applications where it is important to know why a model made a particular prediction.
The increasing complexity of deep learning models has led to a growing need for transparency and interpretability. While these models excel in various tasks, understanding why a neural network makes a specific decision can be challenging. This is where techniques like Layer-wise Relevance Propagation (LRP) come into play.
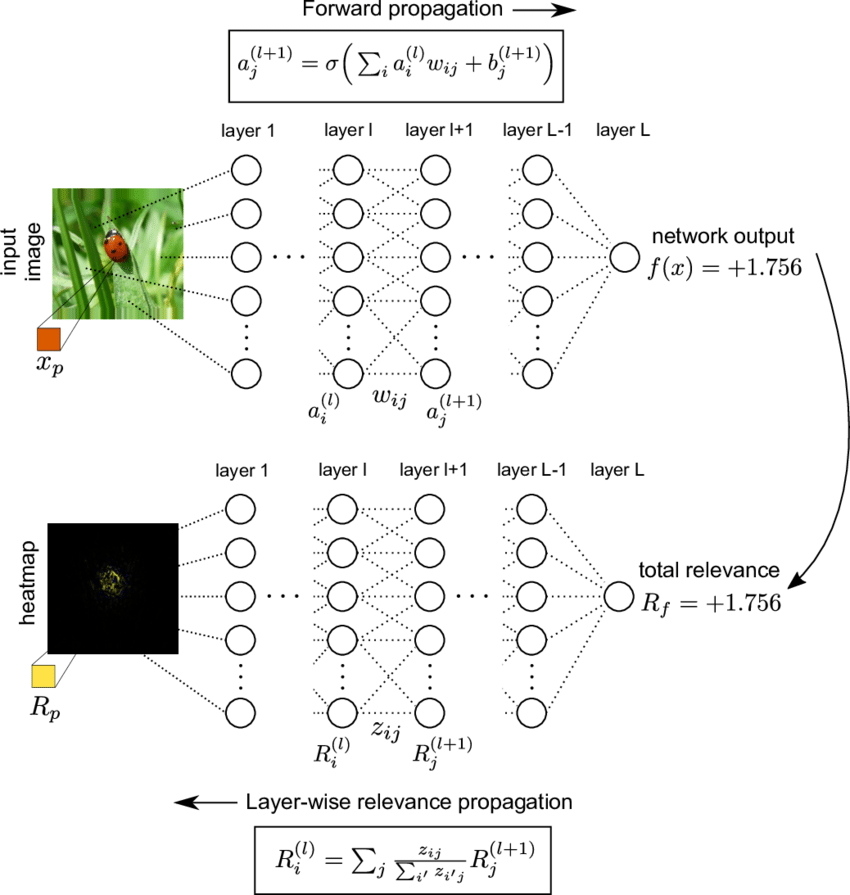
LRP is a technique that can be used to explain the predictions of deep learning models. LRP works by backpropagating the relevance of the output prediction to the input features, layer by layer. This results in a heatmap that shows which input features contributed the most to the prediction, and how much each feature contributed.
Understanding LRP
Layer-wise Relevance Propagation is a technique designed to explain the output of a neural network by attributing relevance scores to each input feature or neuron. It allows us to trace back and understand which components of the input data contributed to a particular prediction or decision. Let’s delve into the key principles and features of LRP:
- Relevance Assignment: LRP assigns relevance scores to the output layer, and these scores are then propagated backward through the network’s layers. The assigned relevance quantifies the importance of each component in the decision process.
- Conservation of Relevance: LRP adheres to a fundamental principle called “conservation of relevance.” It ensures that the sum of relevance scores at each layer remains constant as they are propagated backward. This guarantees that relevance is distributed fairly and that no information is lost during the explanation process.
- Rules and Heuristics: Different variants of LRP employ specific rules or heuristics for relevance propagation. These rules are adapted to the network architecture, activation functions, and the task at hand. Variants such as LRP-epsilon, LRP-Z, and Deep Taylor Decomposition offer tailored explanations for different scenarios.
LRP has a number of advantages over other explainability techniques, such as LIME and SHAP. LRP is more efficient to compute, and it can be applied to a wider range of deep learning models. Additionally, LRP heatmaps are often more interpretable than explanations generated by other techniques.
Here is an example of how LRP can be used to explain the prediction of a deep learning model that is trained to classify images of cats and dogs:
LRP heatmap for cat image
The LRP heatmap shows that the model’s prediction that the image is a cat was most influenced by the pixels in the ears and eyes of the cat. The model also paid some attention to the nose and mouth of the cat, but to a lesser extent.
LRP can be used to explain the predictions of deep learning models in a variety of domains, including computer vision, natural language processing, and medical imaging. It is a valuable tool for understanding the behavior of deep learning models and for increasing trust in their decisions.
Here are some of the benefits of using LRP to explain deep learning models:
- LRP is efficient to compute. This means that it can be used to explain the predictions of large and complex deep learning models in real time.
- LRP can be applied to a wide range of deep learning models. This includes models that are trained on different types of data, such as images, text, and audio.
- LRP heatmaps are often more interpretable than explanations generated by other techniques. This is because LRP heatmaps show how much each input feature contributed to the prediction, and in what direction
Applications of LRP
- Model Debugging: LRP can help identify issues and challenges within neural networks. When a model’s predictions are incorrect or unexpected, LRP offers insights into why these errors occur, helping developers fine-tune their models.
- Bias and Fairness Analysis: LRP can reveal how neural networks are affected by bias in the training data. By analyzing the relevance assigned to various features, it’s possible to detect and mitigate bias and fairness issues in machine learning systems.
- Trust and Transparency: LRP contributes to building trust in AI systems. When neural networks provide clear and interpretable explanations for their predictions, users, stakeholders, and regulators can have more confidence in their decisions.
- Error Analysis: In scenarios where neural networks make unreliable predictions, LRP can pinpoint the sources of uncertainty or errors. This aids in understanding the model’s limitations and guiding improvements.
Challenges and Future Directions
While Layer-wise Relevance Propagation is a powerful tool for model interpretability, it has some limitations. The choice of relevance propagation rules can impact the results, and LRP may not always provide straightforward explanations for complex model behavior. Future research is focused on enhancing LRP’s capabilities, addressing its limitations, and developing more universally applicable rules.
In an age of increasingly complex neural networks, understanding why models make particular decisions is crucial. Layer-wise Relevance Propagation (LRP) is a valuable technique for enhancing model transparency, reliability, and accountability. By attributing relevance scores to individual features and neurons, LRP makes deep learning models more interpretable, enabling us to trust and use them in a broader range of applications. As research in this field advances, we can expect LRP to play an even more significant role in making AI systems understandable and justifiable.
Leave a comment