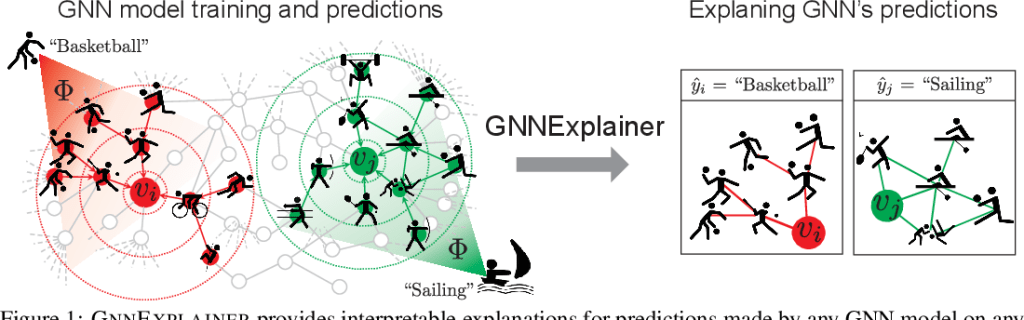
Graph neural networks (GNNs) are a powerful type of machine learning model that can be used to learn from and make predictions on graph-structured data. GNNs are used in a wide variety of applications, including social network analysis, fraud detection, and drug discovery.
However, GNNs can also be complex and difficult to understand. This can make it challenging to trust their decisions, especially in critical applications where it is important to know why a model made a particular prediction.
GNNExplainer is a model-agnostic explainability method for GNNs. This means that it can be used to explain the predictions of any GNN model, regardless of its architecture or training procedure.
GNNExplainer works by learning soft masks for edges and node features in the input graph. These masks indicate which edges and features are most important for the model’s prediction. GNNExplainer then generates a new graph by combining the original graph with the learned masks. This new graph is then passed to the model, and the model’s prediction on the new graph is compared to its prediction on the original graph.
The difference between the model’s predictions on the two graphs is used to explain the model’s prediction on the original graph. For example, if the model’s prediction on the new graph is significantly different from its prediction on the original graph, then this indicates that the corresponding edges and features are important for the model’s prediction.
GNNExplainer has been shown to be effective at explaining the predictions of GNNs on a variety of tasks, including node classification, graph classification, and edge prediction. It is a valuable tool for understanding the behavior of GNN models and for increasing trust in their decisions.
Here are some of the benefits of using GNNExplainer to explain GNN predictions:
- Model-agnostic: GNNExplainer can be used to explain the predictions of any GNN model, regardless of its architecture or training procedure.
- Interpretable explanations: GNNExplainer generates explanations that are easy to understand, even for users who are not familiar with machine learning.
- Effective for a variety of tasks: GNNExplainer has been shown to be effective at explaining the predictions of GNNs on a variety of tasks, including node classification, graph classification, and edge prediction.
Here is how GNNExplainer works:
- GNNExplainer first learns soft masks for edges and node features in the input graph. This is done by training a separate neural network to predict the importance of each edge and node feature for the model’s prediction. The neural network is trained on a dataset of graphs and their corresponding labels.
- GNNExplainer then generates a new graph by combining the original graph with the learned masks. This is done by multiplying the edge weights and node features by the corresponding masks.
- GNNExplainer then passes the new graph to the GNN model and obtains the model’s prediction on the new graph.
- GNNExplainer then compares the model’s prediction on the new graph to its prediction on the original graph. The difference between the two predictions is used to explain the model’s prediction on the original graph.
For example, if the model’s prediction on the new graph is significantly different from its prediction on the original graph, then this indicates that the corresponding edges and features are important for the model’s prediction.
GNNExplainer is a powerful and versatile explainability method for GNNs. It can be used to explain GNN predictions for a variety of tasks, and it is easy to use and understand.
Here are some examples of how GNNExplainer can be used to explain GNN predictions:
- Node classification: If a GNN model is used to predict whether a node in a social network is a bot account, GNNExplainer can be used to explain which features of the node and its neighbors are most important for the model’s prediction.
- Graph classification: If a GNN model is used to predict whether a molecule is toxic, GNNExplainer can be used to explain which atoms and bonds in the molecule are most important for the model’s prediction.
- Edge prediction: If a GNN model is used to predict whether there is a link between two nodes in a social network, GNNExplainer can be used to explain which features of the two nodes and their shared neighbors are most important for the model’s prediction.
GNNExplainer is a valuable tool for understanding the behavior of GNN models and for increasing trust in their decisions.
Leave a comment