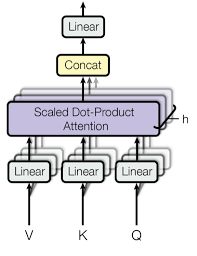
Photo credits: https://paperswithcode.com/method/multi-head-attention
Multi-head attention is a mechanism that allows a model to focus on different parts of its input sequence, from different perspectives. It is a key component of the Transformer architecture, which is a state-of-the-art model for natural language processing (NLP) tasks such as machine translation, text summarization, and question answering.
How multi-head attention works in an encoder
Multi-head attention works by splitting the input sequence into multiple heads. Each head then performs self-attention on its own subset of the input sequence. This allows the model to learn different relationships between the words in the input sequence, from different perspectives.
The outputs of the multiple heads are then combined to produce a single output. This output is then used as the input to the next layer of the encoder.
Self-Attention – A Single Lens Focus:
Imagine you’re reading a mystery novel. When you encounter the phrase, “He didn’t trust him because he knew the secret,” you’ll naturally pay attention to both occurrences of “he” to decipher their referents. This is what self-attention does—it assigns attention scores to various words in relation to a particular word in a sequence.
Example:
For the word “knew” in the sentence, self-attention may give higher weights to both occurrences of “he” to derive its contextual meaning.
Multi-Head Attention – Multiple Lenses for Various Aspects:
Now, think of reading the same novel, but this time you wear a set of different colored glasses, one after the other. Each color lets you focus on different details: one brings out emotional undertones, another emphasizes relationships, and a third might highlight the chronological sequence of events.
In the context of our sentence, with multi-head attention:
- First Head (Relationships): Might focus on “trust” and the two “he” tokens to understand the relationship dynamics.
- Second Head (Emotion): Might emphasize “didn’t” and “secret” to capture the underlying emotions.
- Third Head (Chronology): Could focus on “because” to understand the sequence of events.
Step by Step with Multi-Head Attention:
- Multiple Projections:
- Original word embeddings are transformed into different sets of Q, K, and V vectors for each head.
- For our sentence, each head will have its own set of these vectors, potentially capturing different aspects of the data.
- Parallel Self-Attention:
- Each head independently processes the data using its own Q, K, and V vectors.
- In our example, each head will have different attention scores for the word “knew” based on its unique perspective.
- Concatenation:
- After processing, outputs from all heads are combined.
- This merged output ensures insights from all ‘glasses’ (heads) are considered.
- Linear Transformation:
- This step integrates and refines the concatenated information into a single output.
Why is Multi-Head Attention Valuable?:
- Comprehensiveness: By capturing different perspectives simultaneously, multi-head attention provides a richer understanding of the context.
- Flexibility: Different tasks might benefit from different aspects of the data, and having multiple heads allows transformers to be versatile.
Therefore, if self-attention is akin to a detailed analysis by one expert, multi-head attention is like gathering insights from several specialists, each providing a unique viewpoint, ensuring no nuance is overlooked. Imagine that you are a doctor and you are trying to diagnose a patient’s illness. You can think of self-attention as a single expert who is trying to diagnose the patient’s illness by looking at all of the patient’s symptoms. Multi-head attention is like a team of specialists who are each looking at the patient’s symptoms from a different perspective. The team of specialists then comes together to discuss their findings and make a diagnosis.
So, multi-head attention has a number of benefits for the encoder of a Transformer model. First, it allows the model to learn different relationships between the words in the input sequence, from different perspectives. This helps the model to better understand the meaning of the input sentence.
Second, multi-head attention helps to reduce overfitting. This is because the model is learning different relationships between the words in the input sequence, from different perspectives. This makes the model less likely to memorize the training data and more likely to generalize to new data.
Multi-head attention is a powerful mechanism that can be used to improve the performance of NLP models. It is a key component of the Transformer architecture, which is a state-of-the-art model for many NLP tasks.
Leave a comment