Photo Credits: https://data-science-blog.com/blog/2021/04/07/multi-head-attention-mechanism/
Transformers have revolutionized the field of natural language processing (NLP) by providing a powerful architecture for capturing contextual information in sequences. Two essential components of the Transformer model that enable this contextual understanding are self-attention and multi-head attention. In this article, we will explore the differences between self-attention and multi-head attention, their significance in Transformers, and their applications in various NLP tasks.
Understanding Self-Attention in Transformers:
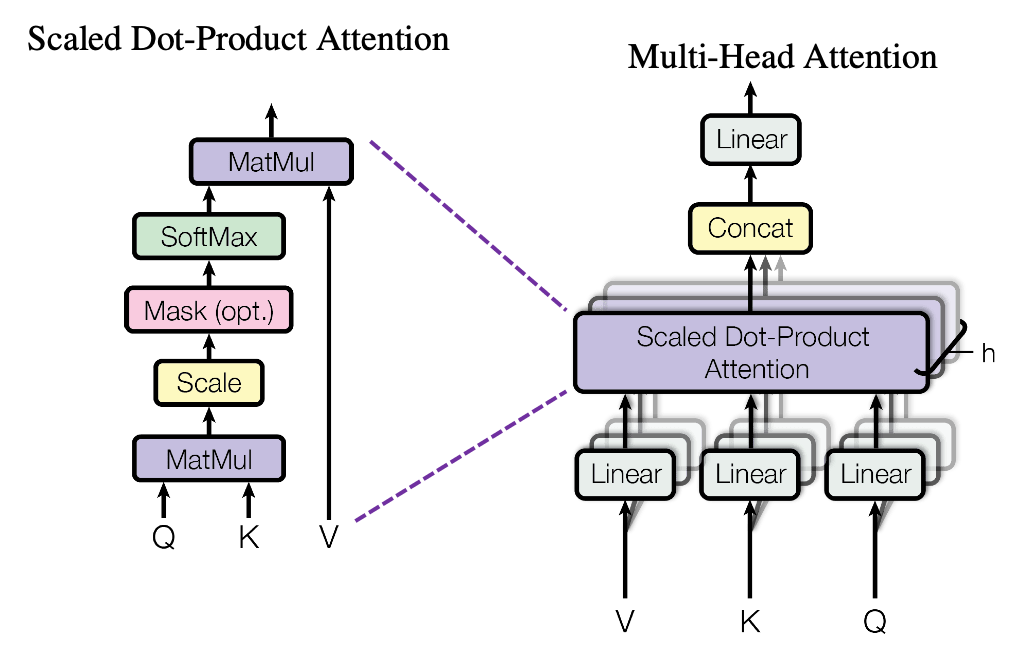
Self-attention, also known as intra-attention, is a mechanism that allows Transformers to weigh the importance of different parts of a sequence while generating representations. It enables the model to capture dependencies between different tokens in the sequence, regardless of their positions. In self-attention, each token in the input sequence attends to all other tokens to determine its representation.
Significance of Self-Attention:
- Capturing Long-Range Dependencies: Self-attention allows Transformers to capture long-range dependencies effectively. Tokens can attend to any other token in the sequence, allowing the model to establish relationships between distant words or subwords. This capability is crucial for tasks that require understanding the overall context, such as machine translation or text summarization.
- Parallel Computation: Self-attention enables parallel computation within Transformers. Each token’s representation can be computed independently based on the attended information, allowing for efficient parallel processing on modern hardware architectures. This parallelization significantly speeds up training and inference for large-scale models.
- Contextual Understanding: Self-attention provides a holistic view of the sequence by considering the importance of each token in the context of the entire sequence. The model can weigh the relevance of different tokens and generate contextual embeddings that capture the relationships between words. This contextual understanding enhances the model’s ability to generate accurate and coherent outputs.
Understanding Multi-Head Attention in Transformers:
Multi-head attention extends the concept of self-attention by employing multiple sets of attention weights in parallel. Instead of relying on a single attention mechanism, multi-head attention allows the model to attend to different parts of the input sequence simultaneously. Each attention head focuses on different aspects of the input, enhancing the model’s representation learning capabilities.
Significance of Multi-Head Attention:
- Enhanced Representation Learning: Multi-head attention enables Transformers to learn multiple representations simultaneously. Each attention head attends to different parts of the input sequence, capturing various types of dependencies. This diversity of attention heads allows the model to capture different aspects of the input and generate more comprehensive representations.
- Increased Model Capacity: By employing multiple attention heads, multi-head attention increases the capacity of the model to capture complex relationships in the data. The model can combine the information from different attention heads to generate more expressive and nuanced representations, leading to improved performance in various NLP tasks.
Applications of Self-Attention and Multi-Head Attention:
- Machine Translation: Self-attention and multi-head attention are crucial in machine translation tasks. Self-attention helps the model capture the dependencies between words in the input sentence, while multi-head attention enables the model to attend to different parts of the input and generate comprehensive representations. This allows the model to accurately translate sentences between different languages.
- Text Summarization: Self-attention and multi-head attention are instrumental in text summarization tasks. The model can attend to relevant parts of the input document while generating a concise summary. This attention mechanism helps the model capture important information and generate informative summaries.
- Question Answering: Self-attention and multi-head attention are employed in question answering tasks. The model can attend to different parts of the input question and context while generating accurate answers. This allows the model to understand the question and generate relevant responses based on the context.
- Sentiment Analysis: Self-attention and multi-head attention are useful in sentiment analysis tasks
- where the model needs to capture the sentiment and emotional context of the input text. By attending to different parts of the input sequence, the model can capture the dependencies between words and generate representations that reflect the sentiment accurately.
Therefore, self-attention and multi-head attention are vital components of the Transformer model in natural language processing. Self-attention allows the model to capture long-range dependencies and establish contextual understanding, while multi-head attention enhances representation learning and increases model capacity. Their applications span various NLP tasks, including machine translation, text summarization, question answering, and sentiment analysis. Understanding the significance and applications of self-attention and multi-head attention empowers researchers and practitioners to leverage the power of Transformers and advance the capabilities of language understanding and generation. #NLP #Transformers #SelfAttention #MultiHeadAttention #MachineTranslation #TextSummarization #QuestionAnswering #SentimentAnalysis
Leave a comment