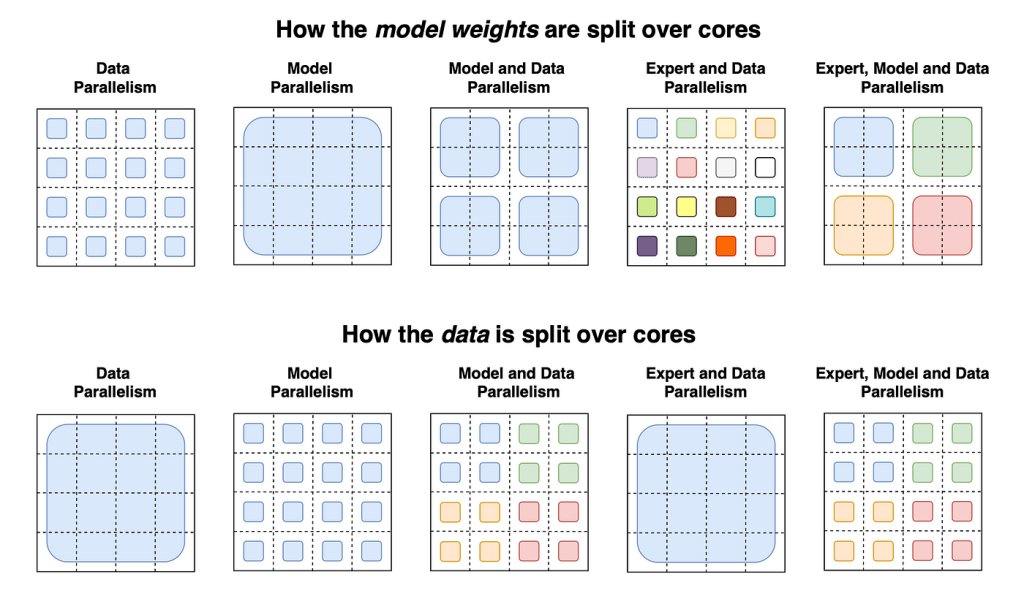
Photo Credits: https://towardsdatascience.com/distributed-parallel-training-data-parallelism-and-model-parallelism-ec2d234e3214
Training large-scale language models, such as GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer), often requires handling models that exceed the memory capacity of a single device. Model parallelism is a technique commonly used to address this challenge by partitioning the model across multiple devices or machines. In this article, we will explore how model parallelism can be achieved in training GPT models, discussing the underlying concepts, implementation strategies, and providing examples to illustrate its practical application.
Understanding Model Parallelism:
Model parallelism is a parallel computing technique that involves dividing the model itself across multiple devices and performing computations independently on each device. In the context of training GPT models, this means splitting the layers or components of the model across different devices, with each device responsible for computing the activations and gradients for its assigned portion of the model. The computed gradients are then exchanged between devices to update the shared model parameters.
Implementation Strategies for Model Parallelism in GPT Models:
- Layer Parallelism: In layer parallelism, the layers of the model are partitioned across different devices. Each device is responsible for computing the forward and backward computations for a specific set of layers. The activations and gradients are passed between devices to ensure consistency in the model updates. This approach allows for training models that are larger than the memory capacity of a single device.
- Token Parallelism: Token parallelism is an alternative approach where the model processes different tokens in parallel across multiple devices. Each device is responsible for computing the activations and gradients for a specific subset of tokens. This approach is useful when dealing with extremely large input sequences that cannot fit in the memory of a single device.
Examples of Model Parallelism in GPT Models:
Let’s consider an example of training a GPT model with 12 transformer layers and a total of 1 billion parameters using model parallelism.
Layer Parallelism Example:
- Device 1: Handles layers 1 to 4
- Device 2: Handles layers 5 to 8
- Device 3: Handles layers 9 to 12 During the forward pass, each device independently computes the activations for the assigned layers based on the input. The activations from one device are then passed to the next device to compute the activations for the subsequent layers. During the backward pass, the gradients are computed independently on each device and exchanged between devices to update the shared model parameters.
Token Parallelism Example:
- Device 1: Processes tokens 1 to 1,000
- Device 2: Processes tokens 1,001 to 2,000
- Device 3: Processes tokens 2,001 to 3,000 In token parallelism, each device independently computes the activations and gradients for the assigned tokens based on the input sequence. The computed gradients are then exchanged between devices to update the shared model parameters.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Communication Overhead: Model parallelism requires frequent communication between devices to ensure synchronization and exchange of activations and gradients. Efficient communication protocols and high-speed interconnects are crucial to minimize communication overhead and prevent bottlenecks in performance.
- Load Balancing: Careful consideration must be given to load balancing across devices to ensure that the workload is evenly distributed. Balancing the computation and memory requirements of different layers or tokens is crucial to maintain efficient parallelism and prevent performance degradation.
Benefits of Model Parallelism for GPT Models:
- Scalability: Model parallelism allows for training GPT models that exceed the memory capacity of a single device. By partitioning the model across multiple devices or machines, model parallelism enables seamless scalability and facilitates training on massive models with billions of parameters.
- Resource Utilization: Model parallelism optimizes resource utilization by allowing multiple devices to work in parallel on different parts of the model. This ensures that the computational power of each device is effectively utilized, leading to faster training times and efficient use of hardware resources.
- Memory Efficiency: With model parallelism, the memory requirements for training large-scale GPT models are distributed across multiple devices. This reduces the memory burden on individual devices, making it feasible to train models that would otherwise exceed the memory capacity of a single device.
- Flexibility in Model Design: Model parallelism provides flexibility in designing and training complex GPT architectures. By partitioning the model into smaller components, researchers have the freedom to experiment with different model configurations, layer sizes, or tokenization strategies, enabling innovation and pushing the boundaries of language modeling.
Model parallelism is a powerful technique for training GPT models that exceed the memory capacity of a single device. By dividing the model across multiple devices or machines and performing computations in parallel, model parallelism enables the training of larger models, efficient resource utilization, and flexible model design. Incorporating model parallelism into the training process empowers researchers and practitioners to push the boundaries of language modeling and achieve state-of-the-art results in natural language processing tasks.
ModelParallelism #GPT #DeepLearning #NLP #MachineLearning #Scalability #ResourceUtilization
Leave a comment