Photo Credits: https://www.toptal.com/deep-learning/exploring-pre-trained-models
In recent years, data parallelism has emerged as a crucial technique for training large-scale language models, including GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer). With the increasing demand for more powerful and sophisticated natural language processing models, data parallelism offers a solution to distribute the computational workload across multiple devices or machines, significantly accelerating training and improving scalability. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of data parallelism and explore how it is effectively used in training GPT models.
Understanding Data Parallelism:
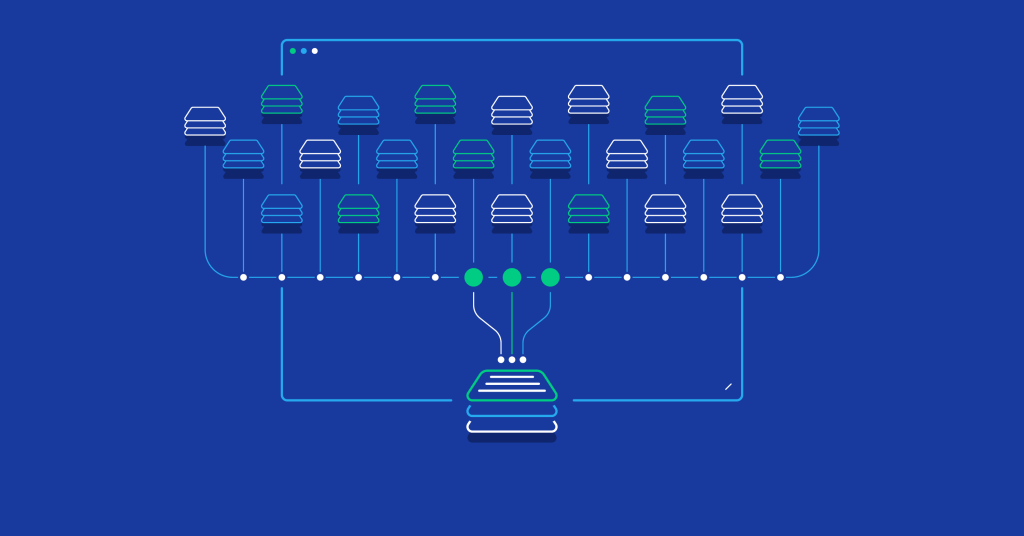
Data parallelism is a parallel computing technique that involves dividing the training data into smaller subsets and processing them concurrently on separate devices. In the context of GPT models, the input text corpus is partitioned into mini-batches, which are then independently processed by multiple devices in parallel. Each device maintains a copy of the model parameters and performs forward and backward computations on its subset of data. The gradients computed on each device are subsequently aggregated to update the shared model parameters, ensuring consistent updates across all devices.
Implementation Strategies for Data Parallelism in GPT Models:
To leverage data parallelism effectively in training GPT models, several implementation strategies are employed:
- Gradient Aggregation:
During the backward pass, each device computes gradients independently based on its subset of data. To synchronize the gradients across devices, various aggregation techniques are used, such as gradient averaging or gradient summation. This ensures that the shared model parameters receive accurate and consistent updates. - Pipeline Parallelism:
In addition to data parallelism, pipeline parallelism can be combined to further enhance training efficiency. In this approach, the model layers are partitioned across devices, allowing for simultaneous forward and backward computations on different parts of the model. This enables overlapping computation and communication, reducing the overall training time. - Batch Size Adjustment:
Data parallelism often requires adjusting the effective batch size to fully utilize the computational resources. Since each device processes a smaller subset of data compared to single-device training, the batch size needs to be increased accordingly. Careful adjustment is crucial to maintain stability during training, as excessively small batch sizes can result in noisy gradients and slower convergence.
Benefits of Data Parallelism in GPT Models:
The utilization of data parallelism offers several significant benefits when training GPT models:
- Faster Training:
By parallelizing the processing of mini-batches across multiple devices, data parallelism enables substantial reductions in training time compared to single-device training. The increased computational power allows for simultaneous computation, accelerating the convergence of GPT models and reducing the time required to achieve desirable performance. - Scalability:
Data parallelism provides a scalable solution for training GPT models on massive datasets or increasing the model size. With the ability to distribute the workload across multiple devices or machines, data parallelism accommodates the growing demands of training state-of-the-art language models, ensuring scalability without compromising performance. - Improved Generalization:
Training GPT models with data parallelism exposes the model to a broader range of training examples by processing diverse mini-batches simultaneously on different devices. This exposure enhances the model’s ability to capture diverse patterns, leading to improved generalization. The model becomes more robust and coherent, generating high-quality outputs across various natural language processing tasks..
Data parallelism has revolutionized the training of GPT models, empowering researchers and practitioners to tackle complex natural language processing challenges effectively. By leveraging the parallel processing capabilities of multiple devices, data parallelism enables faster training, improved scalability, and enhanced generalization. As language models continue to evolve, the utilization of data parallelism will play a vital role in pushing the boundaries of natural language understanding and generation
Leave a comment