In the era of big data, analyzing and extracting meaningful insights from high-dimensional datasets can be challenging. Dimensionality reduction techniques come to the rescue by simplifying the data while retaining its essential information. In this article, we will explore the concept of dimensional reduction, its significance in data analysis, and various popular techniques. We will also delve into real-world examples to illustrate how dimensionality reduction can uncover hidden patterns and improve data-driven decision-making.
Understanding Dimensionality Reduction:
Dimensionality reduction aims to reduce the number of variables or features in a dataset while preserving its inherent structure. By reducing the dimensions, we can overcome the curse of dimensionality, eliminate redundancy, and alleviate computational complexity. This process simplifies data representation and visualization, making it easier to analyze and interpret.
Principal Component Analysis (PCA):
PCA is one of the most widely used dimensionality reduction techniques. It transforms high-dimensional data into a lower-dimensional space by identifying orthogonal components called principal components. These components capture the maximum variance in the data, allowing us to represent the data in a more concise and meaningful way. PCA finds applications in various fields, including image recognition, genetics, and finance.
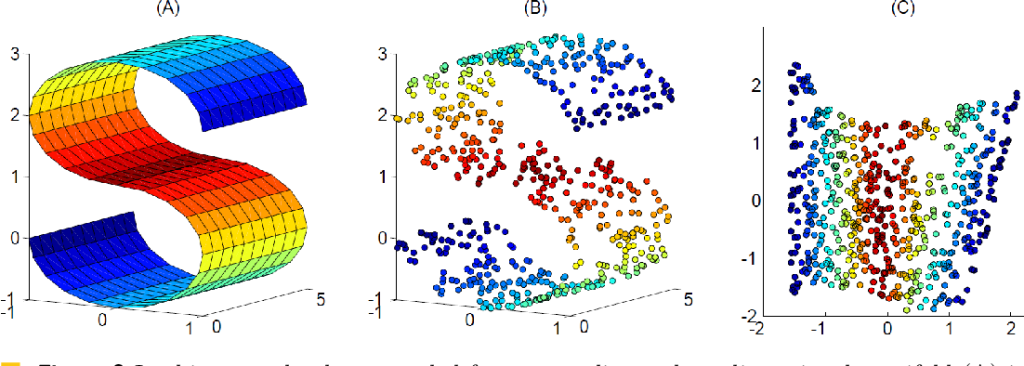
t-SNE (t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding):
t-SNE is a nonlinear dimensionality reduction technique known for its effectiveness in visualizing high-dimensional data in two or three dimensions. It focuses on preserving the local relationships between data points, making it useful for exploring clusters and identifying patterns. t-SNE finds applications in fields like natural language processing, bioinformatics, and social network analysis.
Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA):
LDA is a dimensionality reduction technique that combines dimension reduction with classification. It aims to find a lower-dimensional representation of the data that maximizes the separation between different classes. LDA is commonly used in pattern recognition, face recognition, and sentiment analysis.
Real-World Examples:
a. Image Recognition: In computer vision, dimensionality reduction techniques like PCA and t-SNE are used to analyze and visualize high-dimensional image datasets. These techniques help identify clusters of similar images, detect patterns, and improve image classification accuracy.
b. Customer Segmentation: In marketing, dimensionality reduction techniques can be used to simplify customer data, identify key customer segments, and target marketing campaigns effectively. By reducing the dimensionality of customer attributes, marketers can gain insights into customer behavior, preferences, and purchase patterns.
c. Gene Expression Analysis: In genomics, dimensionality reduction techniques play a vital role in analyzing gene expression data. By reducing the dimensionality, researchers can identify genes that are most relevant to specific diseases, classify patient samples, and discover new biomarkers.
Dimensionality reduction techniques offer powerful tools to simplify complex datasets, improve data analysis, and uncover hidden patterns. From PCA and t-SNE to LDA, these techniques enable data scientists and analysts to gain deeper insights, make data-driven decisions, and solve real-world problems more effectively. By leveraging dimensionality reduction techniques, organizations can streamline their data analysis processes, optimize resource utilization, and unlock the full potential of their data.
Leave a comment