Photo Credits: https://www.arxiv-vanity.com/papers/2002.00388/
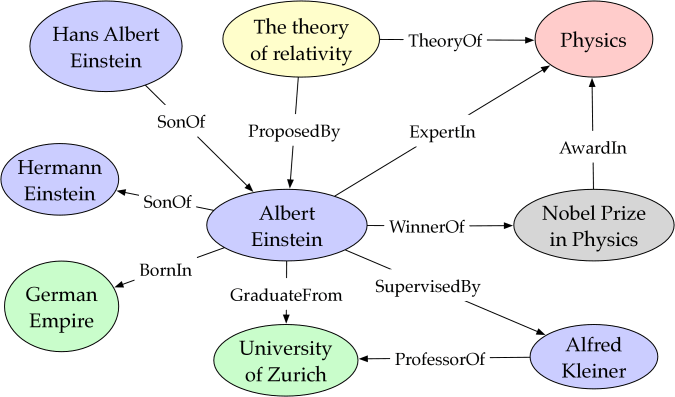
Knowledge graphs serve as powerful representations of structured information, capturing relationships and facts between entities. Knowledge graph completion, the task of predicting missing relationships, plays a crucial role in expanding and enhancing these graphs. DistMult (Distributed Multiplicative) is a prominent knowledge graph embedding model that leverages multiplicative interactions to improve knowledge graph completion accuracy. In this article, we explore the working principles and advantages of DistMult.
Understanding Knowledge Graph Completion:
Knowledge graphs organize information as entities and relationships, forming a network of interconnected nodes. However, knowledge graphs are often incomplete, lacking certain relationships that exist in reality. Knowledge graph completion aims to predict these missing relationships to enhance the comprehensiveness and usefulness of the graph.
Introducing DistMult:
DistMult is a knowledge graph embedding model designed to address the knowledge graph completion task. It operates on the premise that interactions between entities and relationships can be effectively modeled through the element-wise multiplication of their respective embeddings. The model assumes that entity and relationship embeddings reside in a continuous vector space, where their interactions can be captured mathematically.
Key Components of DistMult:
- Entity Embeddings:
DistMult learns low-dimensional embedding vectors for each entity in the knowledge graph. These embeddings represent the semantic properties and characteristics of entities in the vector space. - Relationship Embeddings:
Similar to entity embeddings, DistMult learns embeddings for relationships or predicates. These embeddings capture the semantic meaning and associations between entities. - Scoring Function:
To predict missing relationships, DistMult employs a scoring function based on the element-wise multiplication of entity and relationship embeddings. Specifically, it calculates the score by taking the dot product of the embeddings and sums them up. The resulting score reflects the likelihood or strength of the relationship between the given entities.
Training and Optimization:
During the training process, DistMult adjusts the entity and relationship embeddings to optimize the scoring function. The model leverages observed relationships in the knowledge graph as training data. By minimizing the distance between predicted scores and actual relationships, DistMult learns to represent the relationships accurately in the embedding space.
Advantages of DistMult:
- Capturing Multiplicative Interactions:
DistMult’s use of multiplicative embeddings enables it to capture complex interactions and associations between entities and relationships. The element-wise multiplication allows the model to represent more nuanced semantics, providing a rich representation of the relationships in the knowledge graph. - Scalability and Efficiency:
DistMult is computationally efficient and scalable, making it suitable for large-scale knowledge graphs. Its training process and scoring function computations can be efficiently parallelized, facilitating the processing of massive amounts of data. - Performance and Effectiveness:
DistMult has demonstrated competitive performance in various knowledge graph completion benchmarks and challenges. Its ability to leverage multiplicative embeddings has shown significant improvements in accurately predicting missing relationships, enhancing the completeness and usefulness of knowledge graphs.
Applications of DistMult:
DistMult’s capabilities in knowledge graph completion have wide-ranging applications, including:
- Question Answering Systems: DistMult enables better understanding and retrieval of information by predicting missing relationships in question answering scenarios.
- Recommendation Systems: By completing knowledge graphs, DistMult enhances the recommendation process, facilitating personalized and relevant recommendations based on missing or latent relationships.
- Semantic Search: DistMult aids in improving the accuracy and efficiency of semantic search engines, enabling users to find information more effectively.
DistMult has emerged as a powerful model for knowledge graph completion, leveraging multiplicative embeddings to capture complex interactions between entities and relationships. Its efficiency, interpretability, and scalability make it a valuable tool in various applications that rely on knowledge graphs. As research in knowledge graph embeddings continues to advance, models like DistMult pave the way for deeper insights, better recommendation systems, and more accurate question-answering systems, pushing the boundaries of knowledge representation and reasoning.
Leave a comment